Like Gatsby's green light beckoning across the bay, your dog's eyes hold secrets about their inner world. You've probably noticed how those striking blue-eyed breeds seem to peer right into your soul, and there's actually science behind that intense connection. What you might not know is that eye color links directly to your dog's emotional sensitivity and behavioral patterns. As you begin to understand these connections, you'll discover why some dogs process their world so differently from others.
The Science Behind Blue Eyes in Dogs

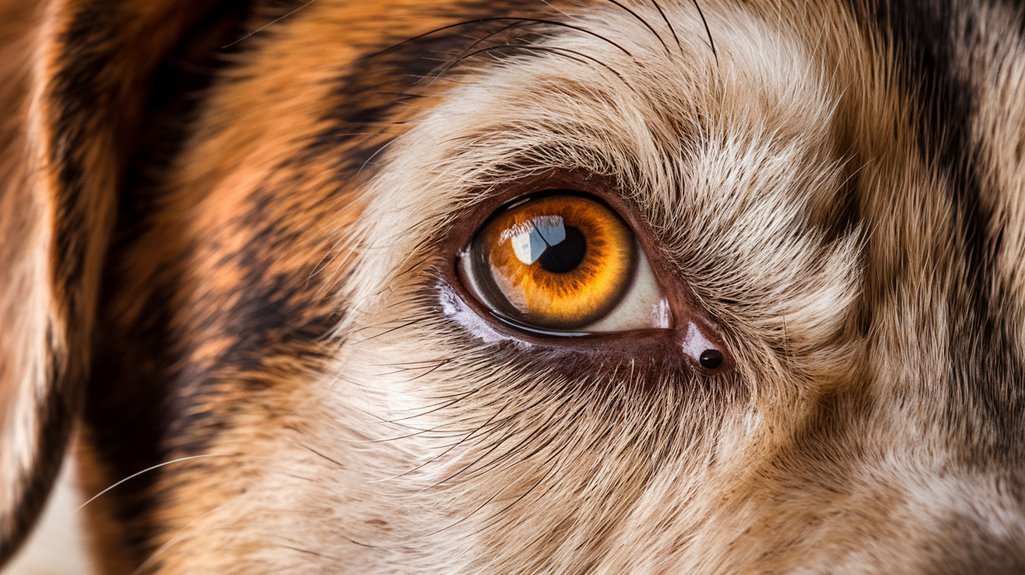
While many dog owners admire their pets' striking blue eyes, the science behind this enchanting trait reveals a fascinating genetic story.
Research shows that a specific genetic mutation on chromosome 18, near the ALX4 gene, disrupts pigment deposition in the iris during development. This discovery emerged from the largest canine genome study ever conducted, analyzing DNA from over 6,000 dogs.
You'll find this mutation isn't exclusive to Siberian Huskies – it appears in various breeds, including Australian Shepherds and Border Collies. This duplication near the ALX4 gene region also influences craniofacial development and hair follicles.
Scientists discovered that just one copy of this genetic variant can result in either completely blue eyes or heterochromia. Recent studies have shown that dogs with blue eyes experience the same oxytocin release when making eye contact with their owners. The mutation, which spans 100 kilobases, explains up to 75% of blue-eyed cases and demonstrates how a single DNA change can create such a distinctive feature in your dog's appearance.
How Eye Color Links to Behavior Patterns
Despite common misconceptions, your dog's eye color can reveal important insights about their behavioral tendencies. Blue-eyed dogs often exhibit specific genetic predispositions that influence their emotional responses and sensory processing abilities.
Recent research examining 214,000 genetic markers in thousands of dogs has provided new insights into the genetic basis of blue eyes. If you have a blue-eyed dog, particularly in breeds like Australian Shepherds or Catahoulas, you might notice they're more prone to anxiety and reactivity. This stems from genetic factors affecting their neurotransmitter function and sensory processing. Dogs with blue eyes may experience vision and hearing impairments that affect their daily behavior.
The merle and piebald genes linked to blue eyes can create behavioral challenges, including heightened vigilance and lower stress thresholds.
Your dog's unique eye color isn't just a cosmetic feature – it's connected to complex genetic mechanisms that shape how they process their environment.
Understanding these connections can help you better support your pet's emotional needs and manage potential anxiety-related behaviors.
Understanding Your Dog's Sensory Processing
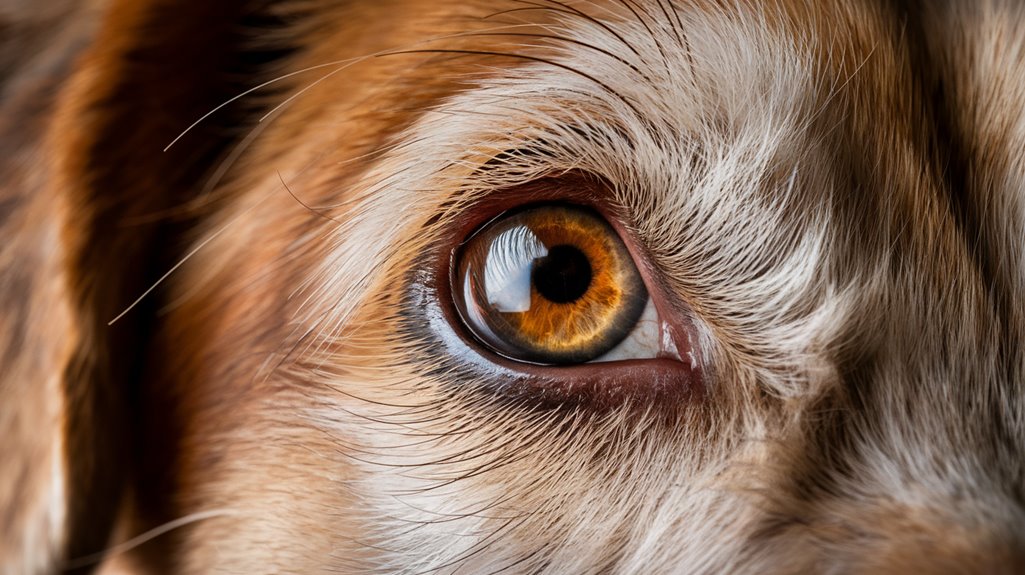

Beyond eye color genetics, your dog's sensory processing abilities shape their daily experiences and behaviors. Dogs with high sensory sensitivity experience their environment more intensely, which can lead to sensory overload and behavior challenges. Research shows that 73% of owners use positive punishment when training their dogs.
Their remarkable olfactory system, containing 250 million scent cells, plays a significant role in canine cognition and emotional responses. Common triggers like loud appliances can make it particularly challenging for sensitive dogs to think and respond clearly.
If your dog seems easily overwhelmed by loud noises, strong smells, or sudden movements, they may have high Sensory Processing Sensitivity (cSPS). This sensitivity can make it harder for them to focus and regulate their emotions.
Your own sensory sensitivity level matters too – if there's a mismatch between you and your dog's sensitivity, it could impact their behavior. Understanding these sensory differences helps you choose appropriate training methods, with positive reinforcement typically working best for sensitive dogs.
What Eye Movement Tells Us About Emotions
As researchers explore deeper into canine behavior, eye movements have emerged as powerful indicators of dogs' emotional states. You'll notice your dog's pupils change size when they encounter different emotional stimuli – larger pupils often signal heightened arousal, especially when they see threatening faces.
When your dog receives oxytocin, they'll find happy faces more appealing and angry faces less intimidating.
Your dog's emotional expression through eye movements isn't just passive – it's an active form of communication with you. While the famous "puppy dog eyes" look might seem deliberate, it's actually more closely tied to natural eye movements than intentional manipulation.
Through eye-tracking studies, we've learned that dogs distinguish between different human emotional expressions, adapting their gaze behavior based on the faces they see.
The Role of Oxytocin in Canine Eye Contact
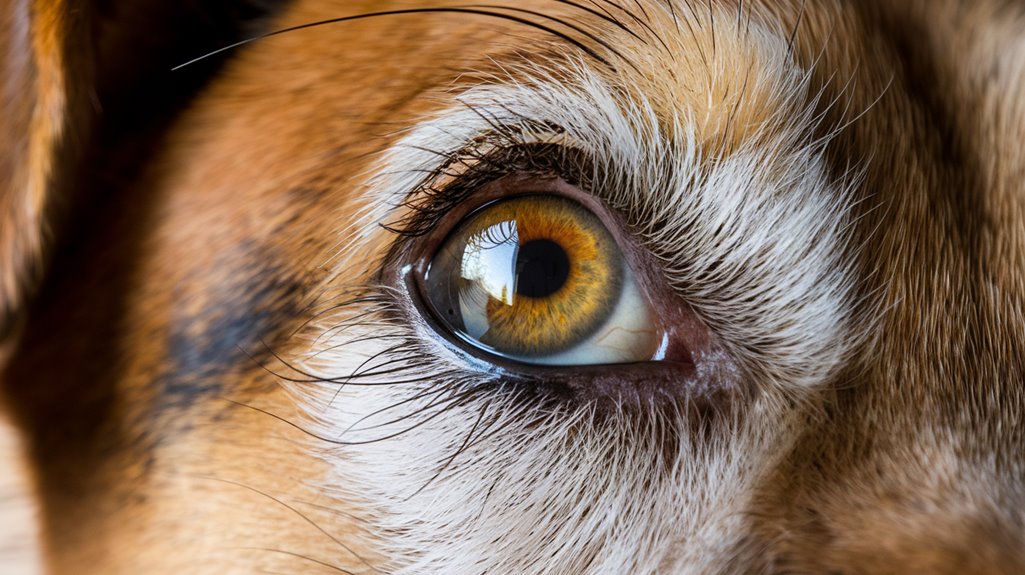

When you gaze into your dog's eyes for more than 2.5 minutes, you'll both experience significant oxytocin effects – your levels surge by 300% while your dog's increase by 130%. This chemical boost strengthens your emotional bonding and builds trust between you.
Female dogs are particularly responsive to oxytocin, showing stronger gazing behaviors with their owners. The interaction produces a positive calming effect on both species. This mirrors the same hormone that helps mothers bond with their babies. Unlike wolves that see eye contact as a threatening signal, dogs have evolved to use gazing as a social bonding tool.
Your dog's response to oxytocin also influences how they perceive your emotions – they'll focus more on your happy expressions and less on angry ones.
Through this hormonal connection, you're creating a powerful feedback loop that deepens your relationship and helps your dog feel more secure in stressful situations.
Separating Eye Color Facts From Fiction
Since many myths surround dog eye color, it's important to understand what science actually tells us.
While eye color misconceptions often link blue eyes to specific personality traits, the reality is more complex. Genetic influences, particularly the merle and ALX4 genes, can affect both eye color and sensory processing simultaneously.
You'll find that a dog's behavior isn't directly determined by eye color, but rather by the underlying genetic factors that influence both traits.
For instance, if your blue-eyed dog shows heightened anxiety, it's likely due to associated sensory processing differences rather than the eye color itself. This is particularly evident in breeds like Australian Shepherds and Catahoula Leopard Dogs, where genetic mutations affecting eye pigmentation can also impact how they process environmental stimuli.
Research shows that dogs with dark-colored irises are generally perceived as more friendly and approachable by humans.