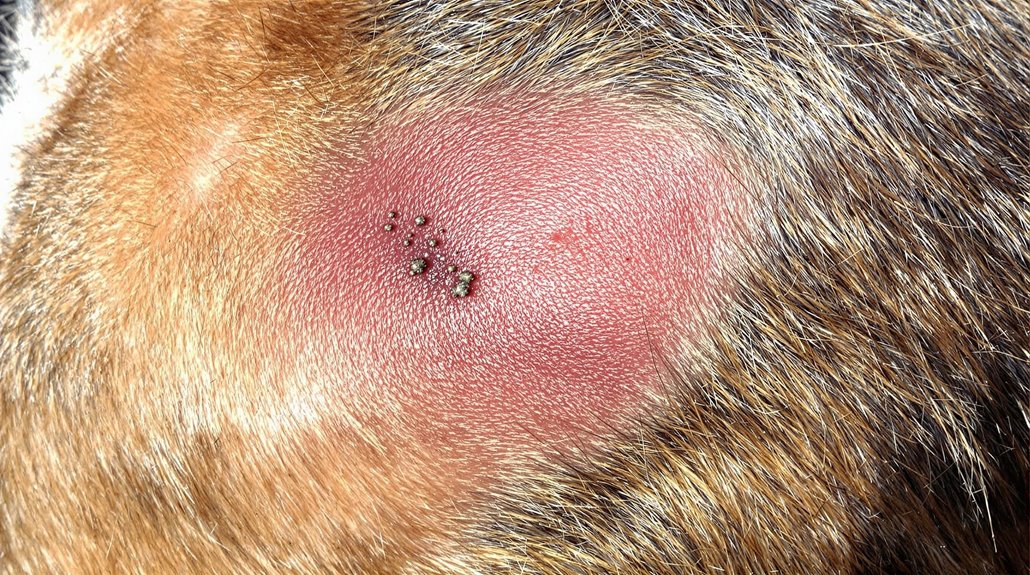
Common dog skin infections show up through symptoms like persistent itching, redness, unusual odors, and hair loss. You'll want to watch for three main types: bacterial (showing pustules), fungal (often in warm, moist areas), and parasitic (caused by fleas or mites). If you notice your dog excessively scratching or licking, along with skin changes or behavioral shifts, it's time to contact your vet. Treatment options include medicated shampoos, antibiotics, or antifungal medications, depending on the specific infection. Regular grooming and preventive care can help avoid future issues, but there's much more to understand about keeping your pet's skin healthy.
Key Takeaways
- Look for common symptoms like persistent itching, redness, swelling, unusual odors, and patches of hair loss to identify skin infections.
- Bacterial infections show pustules and papules, while fungal infections thrive in warm areas and often produce a musty smell.
- Seek veterinary care immediately for open sores, severe behavioral changes, facial swelling, or multiple symptoms occurring simultaneously.
- Treatment options include medicated baths, antibiotics for bacterial infections, antifungal medications, and regular parasite control measures.
- Prevent infections through regular grooming, maintaining clean living spaces, and using appropriate supplements like omega fatty acids.
Understanding Dog Skin Infections
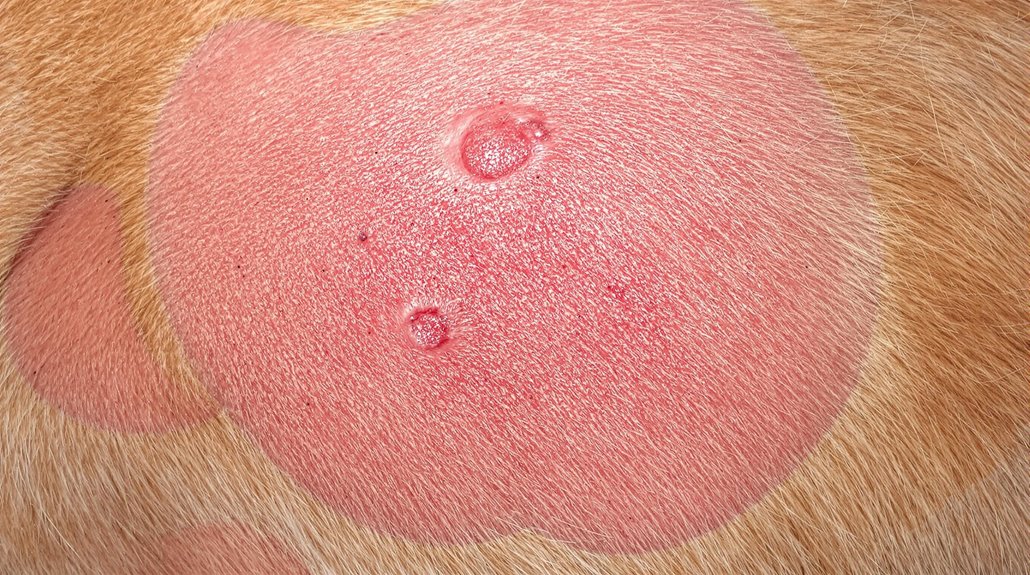
Many dogs experience skin infections throughout their lives, ranging from mild irritations to severe conditions that require immediate veterinary care. Understanding the different types of infections and their causes is essential for proper symptom recognition and timely treatment.
These infections typically fall into four main categories: bacterial, fungal, parasitic, and allergic reactions. Medicated baths can help manage and treat many of these conditions effectively.
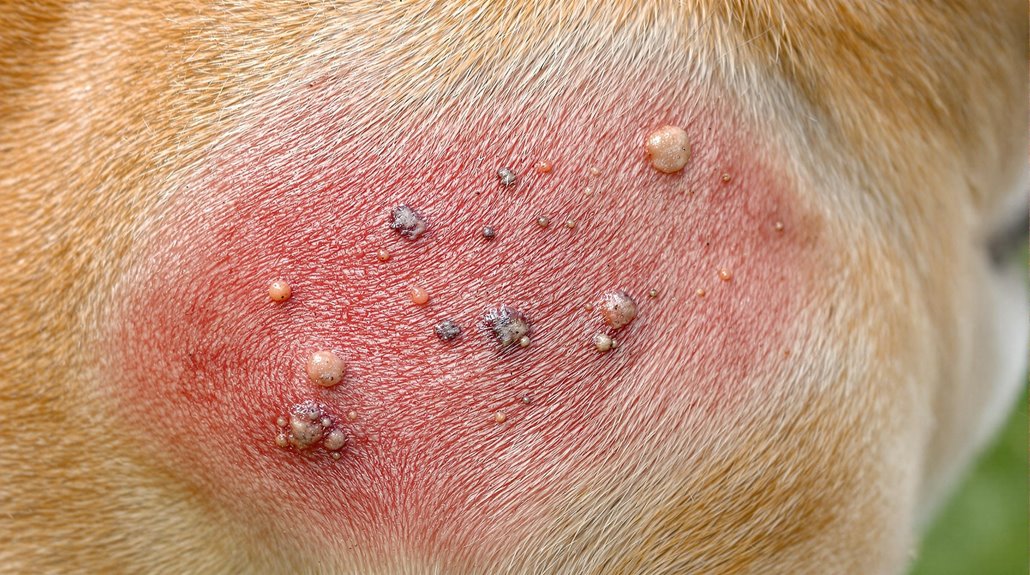
Bacterial infections, particularly pyoderma caused by Staphylococcus pseudintermedius, are among the most common. Fungal conditions like Malassezia and parasitic infections from fleas or mites can also affect your dog's skin health. Your dog's risk of developing these infections increases with certain factors, including broken skin, chronic moisture, and allergies. The most notable signs include papules and pustules that appear as raised, red areas with white centers.
Some breeds are naturally more susceptible to skin infections due to their physical characteristics. If you have a Spaniel, Pekingese, Pug, Bulldog, or Shar-Pei, you'll need to be especially vigilant about infection prevention.
Dogs with skin folds require extra attention, as these areas create warm, humid environments where bacteria thrive. Understanding these risk factors and maintaining proper skin care can help reduce your dog's chances of developing infections.
Signs Your Dog Needs Help
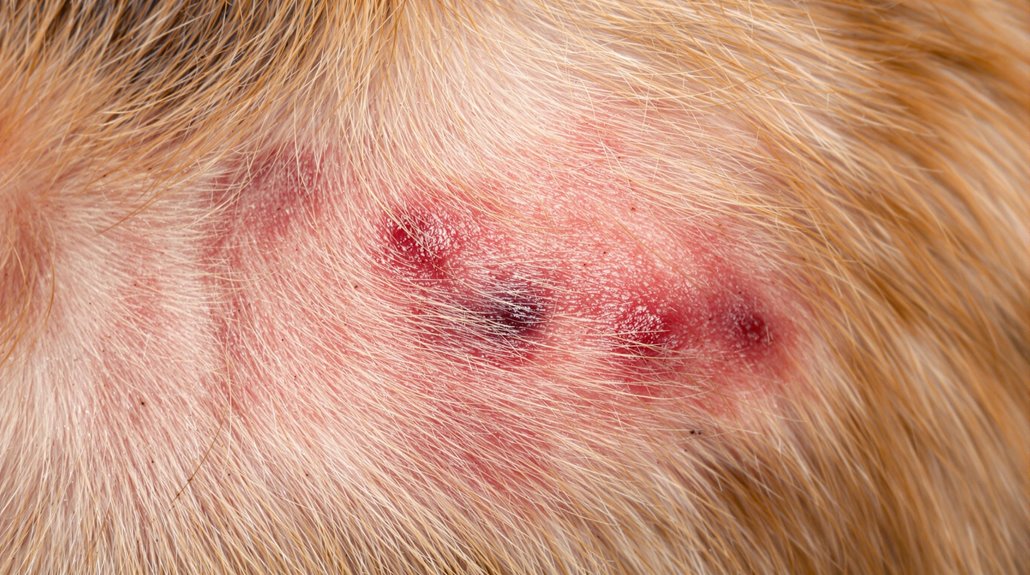
Recognizing the early signs of skin infections in your dog can make the difference between minor treatment and serious complications.
Watch for infection symptoms like persistent itching, redness, swelling, and unusual skin textures. You'll also notice if your dog's skin develops a musty odor or shows patches of hair loss, which often indicate an underlying infection. Yeast dermatitis concerns are especially common in breeds like Poodles and Cocker Spaniels. Good hygiene and early treatment can help prevent infection spread between dogs and humans.
Behavioral signs are equally important indicators that your dog needs medical attention. If you notice your pet becoming more aggressive, anxious, or restless, they may be experiencing significant discomfort from a skin condition.
Pay special attention to excessive chewing or licking of specific areas.
Three critical warning signs that require immediate veterinary care:
- Open sores that don't heal within a few days or show signs of pus
- Severe behavioral changes combined with visible skin irritation
- Multiple symptoms occurring simultaneously, especially if accompanied by systemic infections
Don't wait to seek help if you notice these signs worsening or persisting.
Early intervention can prevent your dog from developing chronic skin problems and guarantee they receive appropriate treatment before the infection becomes severe.
Major Types of Skin Infections
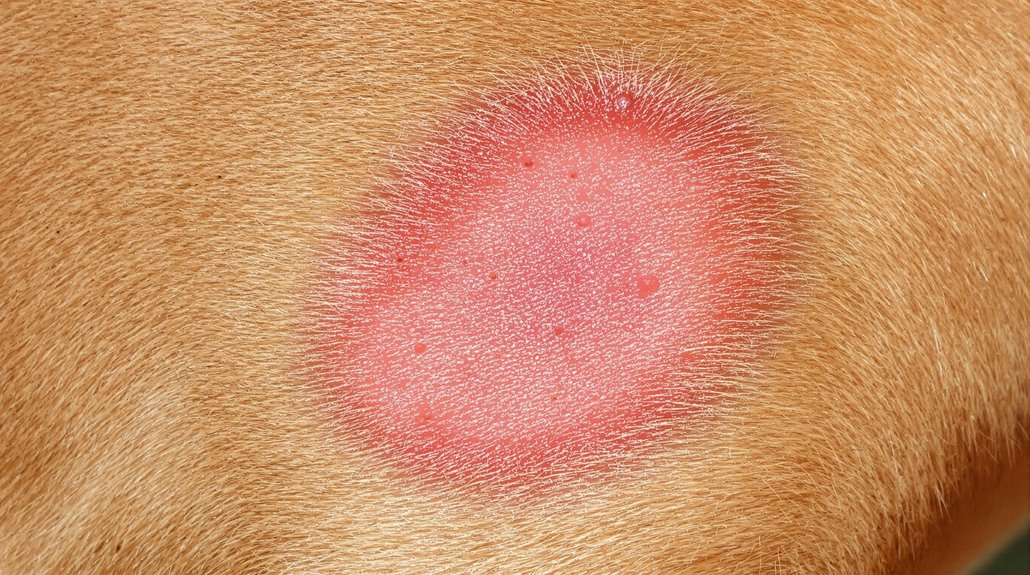
Once you've identified potential skin infection symptoms in your dog, understanding the specific type of infection becomes essential to proper treatment.
Let's explore the four major categories of skin infections that commonly affect dogs.
Bacterial infections, typically caused by Staphylococcus and Streptococcus, present with redness, swelling, and pustules. Hot spots can develop rapidly and appear as moist, painful lesions. Early detection through regular skin monitoring helps improve treatment outcomes. Your dog may need antibiotics and topical treatments to combat these infections.
Fungal infections, including yeast infections and ringworm, thrive in warm, moist areas and cause itching and circular bald patches. You'll need antifungal medications to address these conditions.
Parasitic infestations, such as mange, fleas, and mites, can severely impact your dog's skin health. These parasites cause intense itching and hair loss, requiring specific antiparasitic treatments.
Finally, allergic reactions manifest as atopic dermatitis or contact dermatitis, triggering immune system responses that lead to inflammation and itching. You'll need to identify the allergen and work with your vet to develop an appropriate management plan.
Each type of infection requires different treatment approaches, so it's vital to get an accurate diagnosis from your veterinarian before starting any treatment regimen.
Risk Factors to Watch For
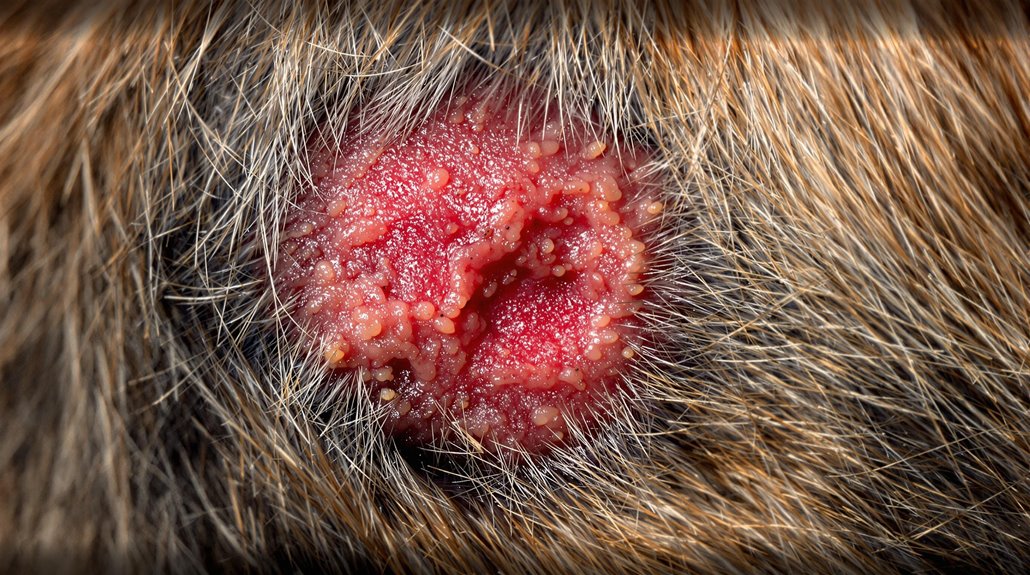
Several key factors can put your dog at higher risk for skin infections, and understanding these risks helps you take preventive action.
Genetic predispositions play a crucial role, with breeds like Lhasa Apso, Dachshund, and West Highland White Terrier being more susceptible to skin issues. Regular bathing with natural oatmeal shampoos can help maintain skin health in predisposed breeds. Age also matters, as older dogs' weakened immune systems make them more vulnerable to infections.
Environmental triggers can greatly impact your dog's skin health. These include allergens, parasites, and even physical injuries. Warm and moist areas of skin, particularly in skin folds, create ideal conditions for bacterial growth.
You'll need to watch for:
- Allergic reactions to food, medications, or environmental factors that can compromise your dog's skin barrier
- Signs of flea, tick, or mite infestations that create entry points for bacteria
- Physical trauma or wounds that increase infection risk, especially in areas where dogs frequently scratch
Your dog's overall health status directly affects their skin's resilience. Chronic diseases, hormonal imbalances, and compromised immune systems can all increase infection risk.
To protect your pet, maintain regular grooming practices, implement proper parasite control, and provide a nutritious diet.
If you notice any skin changes, especially in breeds with known predispositions, consult your veterinarian promptly.
Getting a Proper Diagnosis
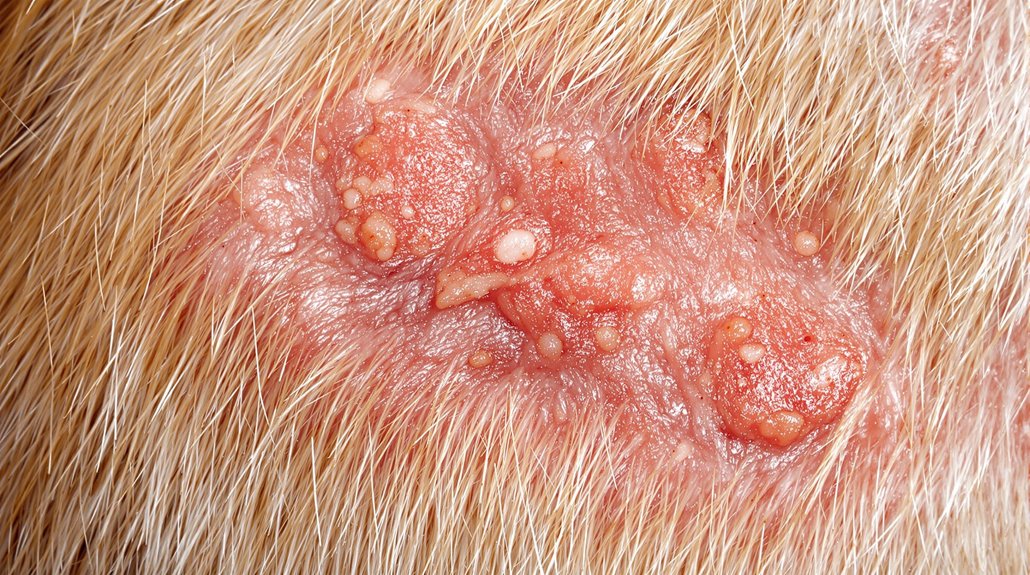
A proper diagnosis of your dog's skin infection requires multiple diagnostic tools and tests that your veterinarian will use to identify the specific cause. Through various diagnostic techniques, your vet can determine whether bacteria, parasites, or fungi are causing the infection. Since infections can be mild to severe, a thorough diagnosis is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment approach. Dermatology specialists typically employ step-by-step guidance when conducting these diagnostic procedures.
| Test Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Skin Scrapes | Identifies mites and parasites like demodex |
| Skin Cytology | Examines cellular material for bacteria and fungi |
| Tape Preps | Collects surface samples of skin and hair |
| Biopsy | Determines antibiotic selection |
| Trichography | Evaluates hair shaft conditions |
Your vet will start with a thorough physical examination and review of your dog's medical history. Skin sampling methods include impression smears, cotton swabs, and acetate tape preparations. These techniques help identify specific pathogens, particularly in cases of bacterial or yeast infections.
In some cases, your vet might recommend additional blood work, including a complete blood count and biochemistry profile. Early detection through these diagnostic procedures is essential for successful treatment. You'll need to provide details about any lifestyle changes or symptoms you've noticed, as this information helps your vet tailor the treatment plan to your dog's specific condition.
Treatment Options and Medications
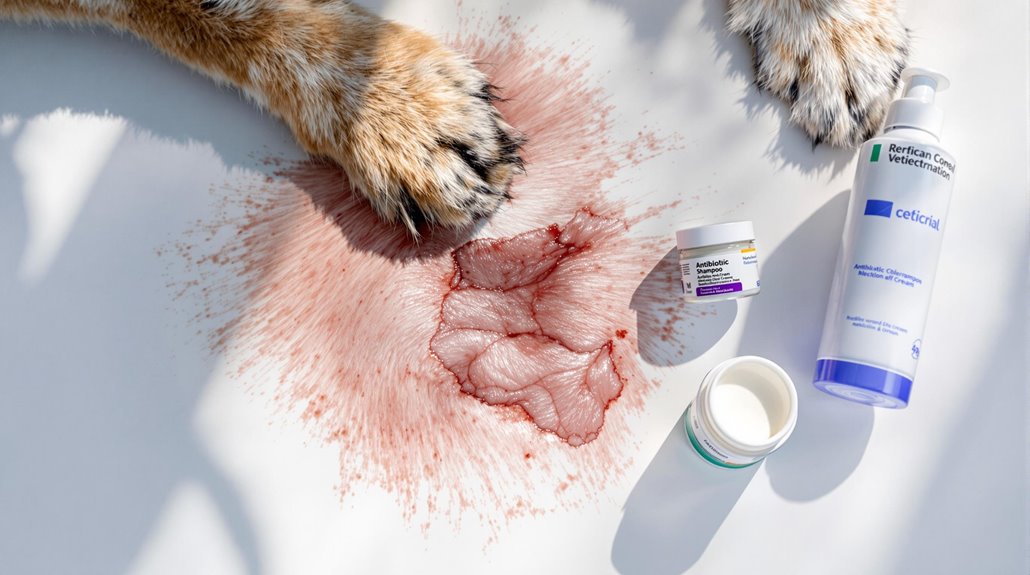

During your dog's treatment for skin infections, you'll likely encounter both topical and systemic medication options. Your vet will determine the best approach based on infection severity, often combining treatments for ideal results.
For bacterial infections, chlorhexidine shampoos (2-4%) work well for surface-level cases, while deeper infections require systemic antibiotics like amoxicillin/clavulanate. It's essential to obtain these medications through veterinary prescription only to ensure proper dosing and safety. To prevent antibiotic resistance, your vet may perform culture testing before prescribing medication.
For fungal infections, antifungal efficacy depends on proper medication selection and consistent application. You'll need to use medicated shampoos containing ingredients like ketoconazole or miconazole, possibly combined with oral medications for severe cases. Regular blood work helps monitor your dog's liver function during treatment. In cases of yeast dermatitis, watch for signs of musty skin odor as an indicator of infection progression.
Key steps for successful treatment include:
- Following the prescribed treatment duration, even after symptoms improve
- Maintaining a regular bathing schedule with medicated shampoos every 3-5 days
- Attending follow-up appointments to monitor progress and adjust treatment if needed
Remember to inspect your dog's skin regularly and use preventive measures like antiseptic sprays between baths to avoid infection recurrence.
Natural Remedies for Skin Health
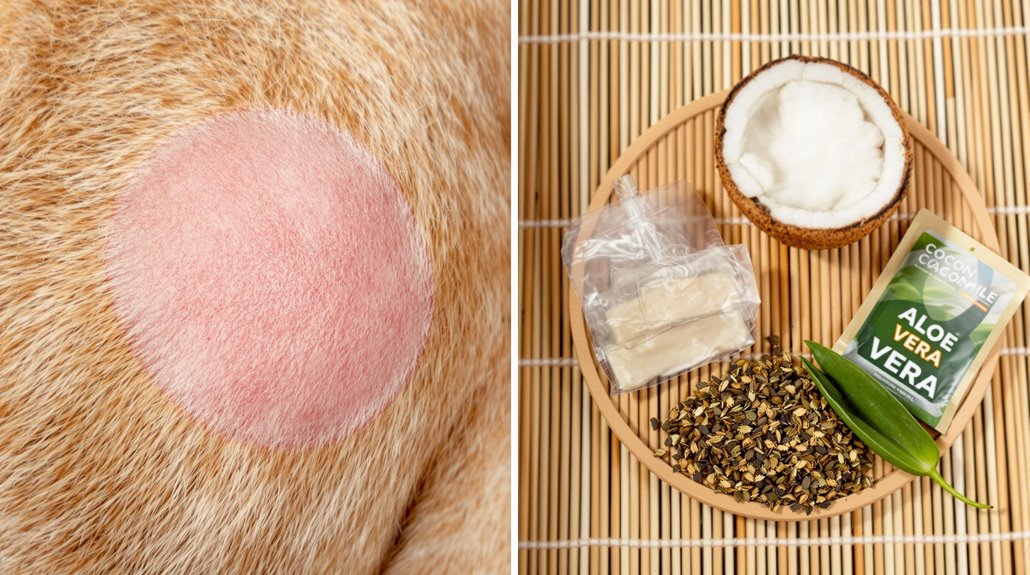
Natural remedies offer gentle yet effective solutions for managing your dog’s skin health alongside traditional treatments. These remedies can help soothe irritation and reduce inflammation, making them a valuable addition to your dog’s skincare routine. For pet owners looking to enhance their dog’s well-being, incorporating seasonal dog paw protection tips is essential, especially during harsh weather conditions. By combining these natural approaches with veterinary guidance, you can ensure your furry friend enjoys optimal comfort and health year-round.
You'll find that coconut oil benefits your pet's skin through its natural antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. Simply apply it directly to affected areas to moisturize, reduce itching, and promote healing, especially if your dog suffers from eczema or insect bites.
Tea soaks provide another soothing option for irritated skin. You can use lukewarm chamomile, green tea, or calendula tea for a five-minute soak. If bathing isn't practical, apply the tea directly to itchy spots using a clean cloth. Consider using an equal parts mixture of apple cider vinegar and water as a spray for additional skin relief.
Pure aloe vera gel works effectively for minor skin irritations and hot spots. Apply it directly to affected areas, but watch for any adverse reactions. Adding a fish oil supplement to your dog's diet can help improve skin health from within.
For widespread itching, colloidal oatmeal offers significant relief. Create a milky bath solution and let your dog soak for about 10 minutes, making sure to gently massage the mixture into problem areas. Remember to rinse thoroughly and pat dry.
These natural remedies can complement veterinary treatments, providing your dog with gentle, chemical-free relief from skin discomfort.
Prevention and Regular Care
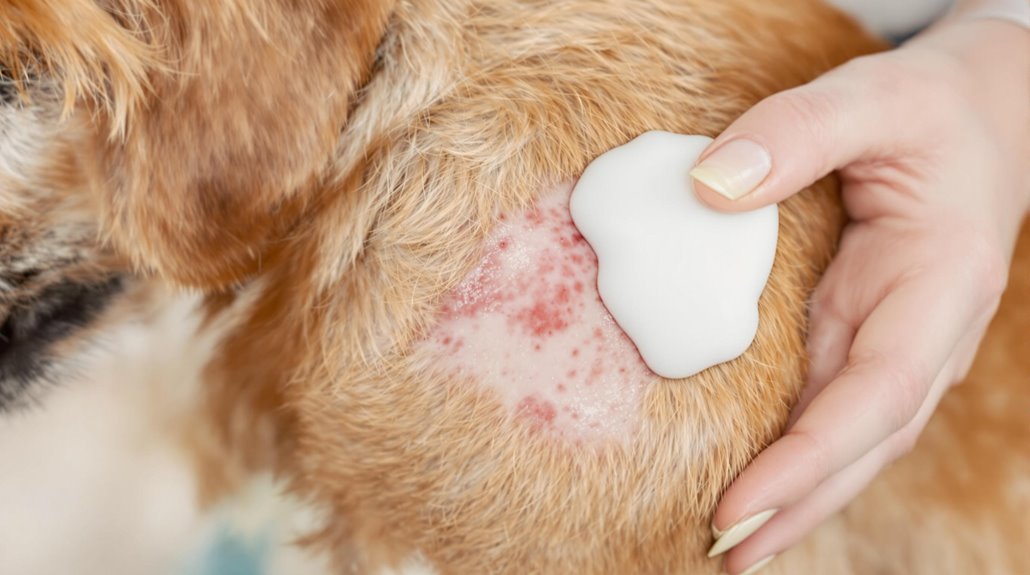
Preventing skin infections in your dog requires four essential care practices: regular grooming, proper bathing, consistent monitoring, and maintaining a clean environment.
Preventive grooming isn't just about keeping your pet looking good – it's vital for removing allergens, dirt, and excess oils that can lead to infections. You'll need to adjust your brushing schedule based on your dog's breed and coat type. Breeds like poodles and cocker spaniels require extra attention since they are prone to yeast infections. Regular brushing stimulates natural oils and helps maintain healthy skin.
When it comes to bathing, don't overdo it. While regular baths are important, too much bathing can strip natural oils from your dog's skin. Use pH-balanced shampoos specifically formulated for dogs, and consider dry shampoo between baths.
Dietary supplements, particularly omega fatty acids, can strengthen your dog's immune system and promote healthy skin.
Here are three key prevention strategies to implement immediately:
- Inspect sensitive areas daily, including ears, paws, and underbelly
- Keep your dog's living space clean and free from allergens
- Use products containing lipids and emollients to maintain the skin barrier
Regular veterinary check-ups are essential for early detection of potential skin issues.
Combine these preventive measures with proper nutrition and consistent grooming to maintain your dog's skin health.
When to Contact Your Veterinarian
While preventive care helps maintain your dog's skin health, knowing when to seek professional help is equally important. Early detection of skin issues can prevent serious complications and guarantee your pet receives proper treatment. Don't wait to contact your veterinarian if you notice persistent skin irritations, chronic ear infections, or unusual masses on your dog's toes. Prescription medications are often necessary to effectively treat persistent skin conditions. Having an understanding of triage levels helps pet owners make informed decisions about the urgency of veterinary care needed.
| Warning Signs | Action Required |
|---|---|
| Facial swelling & breathing difficulty | Immediate emergency care |
| Persistent itching & hair loss | Vet visit within 24 hours |
| Chronic ear infections | Schedule appointment this week |
| Non-healing sores with pus | Same-day vet consultation |
| Unusual skin odors & changes | Evaluation within 48 hours |
While home care practices are essential, certain symptoms require professional attention. Watch for behavioral changes like increased anxiety or aggression, as these can indicate discomfort from skin conditions. If your dog develops hives, severe allergic reactions, or shows signs of skin necrosis, seek emergency care immediately. Regular monitoring of sensitive areas like ears, paws, and underbelly supports early detection of potential issues. When in doubt, it's better to consult your veterinarian than risk complications from delayed treatment.