Your dog's tail isn't just a cute appendage that wags when they're happy – it's actually one of their most crucial communication tools and a window into their well-being. While you might notice the obvious signs of joy or fear, your pup's tail position and movement patterns can reveal subtle clues about their physical health that you won't want to miss. Before you dismiss that slight change in your dog's tail behavior, consider what this essential body part is trying to tell you.
Understanding Your Dog's Tail Language

Everyone knows a wagging tail means a happy dog, but your furry friend's tail actually communicates a complex range of emotions and intentions. Through tail communication, your dog expresses everything from confidence to fear, making their tail anatomy a crucial emotional barometer. Monitoring your dog's tail movements helps you better understand their emotional state and mood.
You'll notice different positions tell distinct stories: a high tail often signals confidence or potential aggression, while a tucked tail indicates fear or submission. Longer tails are especially effective at conveying these emotional signals compared to shorter or curled tails.
Watch for various wag patterns too – a broad, sweeping motion typically means friendliness, but tiny, rapid wags might signal nervousness or impending action.
Remember that breed characteristics and individual personality affect how your dog uses their tail to communicate. For accurate interpretation, you'll need to evaluate other body language cues and environmental factors that influence your dog's tail behavior.
Common Signs of Tail Troubles
How can you tell when your dog's tail needs medical attention? Your furry friend's tail can signal various health issues through both physical and behavioral changes. From tail injuries to specific tail conditions, knowing what to watch for helps you act quickly when problems arise. Since tails help with balance during movement, any difficulty in walking or running may indicate a tail-related health issue. Dogs that experience nerve damage from tail pulling injuries may show signs of incontinence.
- Unusual tail positioning or changes in wagging patterns might indicate muscle strain or injury.
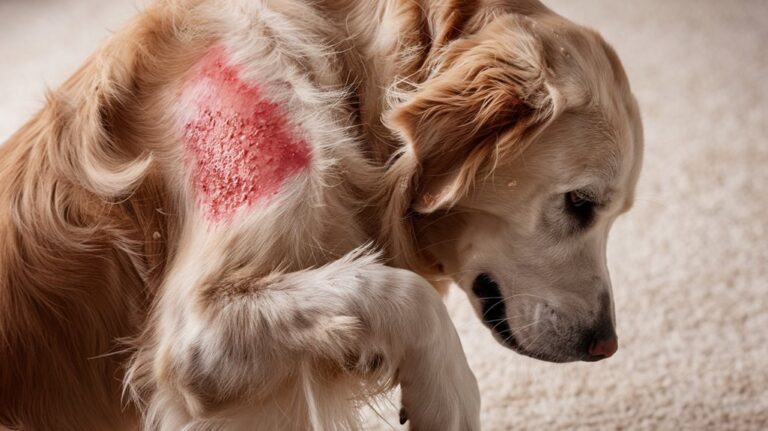
- Constant licking, biting, or hair loss around the tail area suggests discomfort or irritation.
- Happy tail syndrome can cause bleeding ulcers in dogs with long tails.
- Swelling, growths, or masses on the tail require veterinary evaluation.
- Signs of severe pain, like whining or crying, combined with tail problems need immediate medical attention.
Watch for these warning signs and don't hesitate to contact your vet if you notice any concerning changes in your dog's tail behavior or appearance.
The Hidden Connection Between Tail Position and Pain

Your dog's tail position reveals more about their health than you might realize. When it comes to pain assessment, understanding tail movements and positions can help you identify if your furry friend is suffering.
If you notice your dog's tail consistently lowered or tucked, especially during activities like jumping on furniture or climbing stairs, they might be experiencing chronic pain. Environmental factors like stressful situations can make a dog's tail position change dramatically.
Watch for the correlation between their ears and tail – if both are lowered during movement, it's often a sign of discomfort. Young adult dogs may show these changes more noticeably. A key insight from the Ankara University study shows that healthy dogs maintain upward or relaxed tail positions during normal activities.
You'll also want to look for behavioral shifts like reduced activity, excessive licking, or social withdrawal, as these accompany tail position changes in 70% of dogs experiencing pain.
Remember that different health issues can affect tail behavior differently, so consider the whole picture when evaluating your pet's well-being.
When Changes in Tail Movement Signal Health Issues
Beyond simple pain indicators, a dog's tail movements can reveal complex health issues that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Regular gentle brushing sessions can help owners spot any unusual changes or abnormalities during maintenance. Various tail twitching signals and tail posture implications can serve as early warning signs of underlying medical conditions. Accurate interpretation requires understanding that tail signals vary significantly between individual dogs.
Here's what you should watch for:
- Repetitive tail chasing or biting might indicate allergies, injuries, or obsessive-compulsive disorders
- Sudden changes in normal wagging patterns could suggest neurological issues
- Asymmetrical tail movement, especially left-sided wagging, may reveal stress or anxiety disorders
- Complete lack of tail movement might signal spinal problems
- Excessive tail tucking or frozen tail positions could indicate chronic pain or internal discomfort
If you notice these changes persisting for more than a day, it's essential to consult your veterinarian, as early detection often leads to better treatment outcomes.
Steps to Monitor and Protect Your Dog's Tail Health

Maintaining a dog's tail health requires a combination of regular monitoring and proactive care strategies.
Start with consistent tail grooming, brushing the area thoroughly to detect any unusual changes, lumps, or parasites early. This routine helps prevent matting and discomfort while giving you a chance to spot potential issues. Through regular health assessments, you can identify concerning changes before they become serious problems.
Focus on injury prevention by identifying hazards in your dog's environment and supervising them in unfamiliar spaces. Keep an eye on furniture edges and doors that could harm their tail. Your dog's tail movements and positions can indicate their emotional state and well-being.
You'll also want to guarantee your dog gets regular exercise to strengthen their tail muscles and improve overall coordination.
Don't skip veterinary check-ups – they're essential for monitoring your dog's tail health.
If you notice any swelling, unusual movement, or signs of discomfort, contact your vet immediately.